Table of Contents
What is OIDC?
Two of the more prevalent authentication protocols in passwordless authentication systems are OpenID Connect (OIDC) and Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML).
SAML, developed in the early 2000s, has been the go-to standard for Single Sign-On (SSO) for decades, providing a secure exchange of authentication and authorization data between parties. On the other hand, OIDC, a relatively newer protocol built on top of OAuth 2.0, has gained significant traction for its ease of integration with modern web and mobile applications, offering a more lightweight and flexible approach to user authentication.
Despite sharing some functionality similarities and the goal of securing user access, comparing SAML vs. OIDC reveals critical differences that significantly impact authentication processes. To understand them better, we’re going to look under the hood of both protocols and compare them side by side.
What is OIDC?
OIDC (OpenID Connect) is an open protocol that allows applications to verify users' identities using third-party identifiers. It builds on the Open Authorization (OAuth) framework, which lets applications access user account information without requiring their credentials. OAuth itself does not possess the capacity to authenticate users, which is why OIDC was developed and integrated.
Read more: OpenID vs OAuth: Understanding the Difference
How OIDC works
Think of OIDC as a trustworthy bridge between the user, the service they're attempting to access, and the identity provider (IdP), like Google or Facebook.
For example, when a user chooses to log into an online service with their Google account, OIDC helps the service provider (SP) securely communicate with Google to confirm their identity. Once confirmed, OIDC communicates back to the SP that the user is who they claim to be
To transfer this data between the parties, OIDC uses JSON Web Tokens (JWTs).
OIDC makes it easier for end users to access applications or websites without the hassle of creating and managing additional credentials. It ensures a seamless and convenient user experience while maintaining the necessary security measures.

OIDC Use Cases
When should you choose OIDC? Here are some common use cases:
SSO: OIDC enables users to authenticate once with an IdP and access multiple applications without re-entering credentials.
Federated authentication: OIDC can enable primary IdPs to hand off the authentication process to a federated IdP. This can be done without the developers having to change their primary IdP or user stores.
Social login: OIDC allows users to log in to applications using their social media accounts (e.g., Facebook, Google) instead of creating new accounts.
Mobile and native apps: OIDC provides secure authentication for mobile and native applications, delegating the process to an IdP.
API authentication and authorization: OIDC secures APIs by verifying client identities and enforcing access controls based on user roles and permissions.
Read more: Federated Authentication vs. SSO: Choosing the Right Path
What is SAML?
SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) is another open standard predominantly used for authentication and authorization data exchange between IdPs and SPs. It is based on XML (Extensible Markup Language) for the secure transmission of user identity information across different domains.
SAML is widely used in enterprise environments for implementing SSO solutions, allowing users to access multiple applications and services with a single set of credentials. It is particularly useful in scenarios where organizations need to collaborate or provide controlled access to external users.
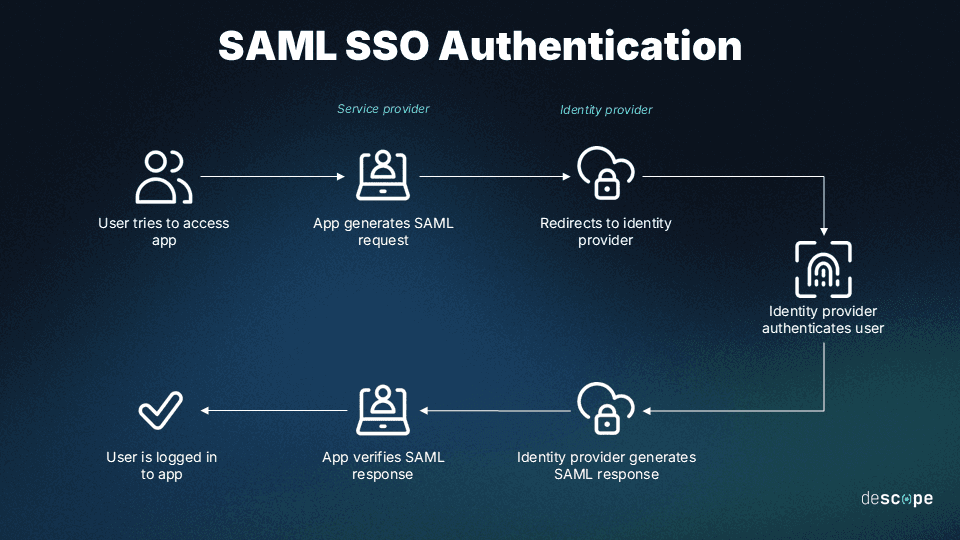
How SAML works
SAML establishes a trust relationship between the IdP and multiple SPs, exchanging information through secure XML-based documents. These XML documents, known as SAML assertions, contain verified information about a user's identity and privileges.
Ultimately, SAML facilitates SSO and reduces the need for multiple usernames and passwords, streamlining access to various services.
SAML Use Cases
SSO: Like OIDC, SAML also enables users to authenticate once and access multiple applications without separate logins, improving convenience and security.
Cross-organizational collaboration: SAML facilitates secure collaboration between organizations or different domains, simplifying access management.
Cloud-based applications: SAML provides SSO for cloud applications, ensuring consistent and secure authentication experiences across various platforms.
Web-based services and portals: SAML enables SSO for web-based services, allowing controlled access without separate user accounts or credentials.
Read more: IdP-initiated vs SP-initiated SSO
Comparing SAML vs. OIDC
OIDC and SAML create a more efficient and secure login process than most traditional password-based authentication systems. However, they differ in how they achieve these outcomes and the specific situations where they are most beneficial. Here’s how they compare:
Basis: OIDC uses RESTful HTTP endpoints and lightweight JWTs, making it well-suited for modern web and mobile applications. SAML, typically used for enterprise SSO, transfers identity and access data through larger and more complex XML documents.
Integration complexity: OIDC tends to be easier to implement and integrate into modern applications due to its use of JSON and RESTful APIs, aligning well with the technologies used in today’s web development. SAML, on the other hand, can be more complex and requires more effort for parsing and handling the data.
Security: Both OIDC and SAML support strong security mechanisms. OIDC’s JWTs can be encrypted and digitally signed. Similarly, SAML relies on XML encryption and digital signatures to secure the assertions. However, generally speaking, SAML is considered to be more secure
| SAML | OIDC |
|---|---|---|
Protocol Differences | SAML transmits XML documents, which can be cumbersome for certain applications. | OIDC uses comparatively lightweight JWTs, requiring minimal processing. |
Use Cases and Applicability | SAML is older and works best in more traditional work environments, like several enterprise programs that work in close conjunction. | OIDC works especially well in environments that feature mobile APIs and single-page applications. |
Security Considerations | SAML has a longer track record of security performance than OIDC. It’s also more feature-rich and flexible to security needs. | OIDC is built upon the OAuth 2.0 authorization framework, providing a flexible security model. |
Scalability and Performance | SAML has been used successfully across many environments for over 20 years. However, its wide applicability to future uses is being debated. | OIDC is leaner and more flexible. It’s designed to work with contemporary and emerging technologies, making it an excellent choice for long-term scalability. |
Choosing between OIDC vs. SAML
From a developer’s perspective, choosing whether to implement OIDC or SAML in authentication flows typically depends upon who the end user is.
Ultimately, the choice often comes down to whether the end users and adopters will require SSO functionality. You can configure apps, websites, and programs to accommodate both SAML/SSO and OAuth/OIDC functionality. But if you have to choose one, here’s how to decide.
When to choose OIDC
If your adopters operate in a contemporary software environment with flexible tech stacks, including many web and mobile applications, then OIDC is likely the best option. Apps that accommodate various end-user devices and exert less control over how users access their profiles will benefit from OIDC.
However, there is always value in accommodating older technology and needs as well. Consider a hybrid approach, leaving room for SAML SSO alongside or in conjunction with OIDC.
When to choose SAML
The most pressing reason to choose SAML over OIDC is that an adopter organization’s existing infrastructure requires it. SAML has been around in its current form (SAML 2.0) since 2005. While updates have improved its functionality and security since then, its basic applicability is essentially the same. Organizations that depend upon more traditional software suites, like desktop programs, often prefer the reliability of SAML.
However, even in these cases, including SAML and OIDC functionality options will help adopters prepare for the more agile, mobile future of enterprise software. Flexibility is key.
Drag-and-drop SAML or OIDC with Descope
In many ways, OIDC is seen as a newer iteration of SAML that does some things differently but also leaves some benefits behind. Neither protocol has replaced the other and is unlikely to do so in the near future.
Both protocols have their unique advantages, with SAML maintaining its relevance in older systems and OIDC excelling in cutting-edge environments. Depending on your user base, it might make sense to incorporate both. However, both protocols can be complex to implement in-house.
With Descope, developers can effortlessly integrate OIDC and SAML authentication into any application or website using just a few lines of code (or in some cases, no code at all).
SAML-based SSO can be added using drag-and-drop workflows, without making any big configuration changes to your app.

OIDC federated authentication with Descope can be used to add passwordless login to existing apps, even if you already have primary identity providers such as Auth0, Amazon Cognito, or Firebase.
Sign up for a Free Forever account with Descope to simplify your auth with SAML, OIDC, or any other protocol you need. Have questions about our platform? Book a demo with our auth experts.