Table of Contents
Enhanced security
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) has become one of the most widely used mechanisms to strengthen traditional, password-based authentication due to the many benefits stemming from proper MFA implementation.
Chief among MFA benefits is enhanced security. Rather than relying solely on passwords to safeguard sensitive information, MFA utilizes at least one more unique possession or inherence factor to authenticate identity and access.
MFA has seen increases in adoption in recent years. In fact, some reports estimate a doubling in MFA use since 2020, despite some highly regulated industries and large organizations lagging behind.
Nevertheless, given the benefits of MFA, it’s expected that these outliers will follow suit sooner rather than later if developers are given straightforward implementation options.
Beyond the bolstered security, those who adopt MFA can tap into other benefits including enhanced accessibility, regulatory compliance, scalability, and user convenience. Let’s take a closer look at each of these advantages.
Enhanced security
The topmost benefit of MFA is that it offers greater security assurance than traditional auth methods. This is because it provides one or more additional layers of security beyond passwords, thus preventing or mitigating:
Phishing attacks
Fraud and identity theft
Weak passwords
Credential leaks
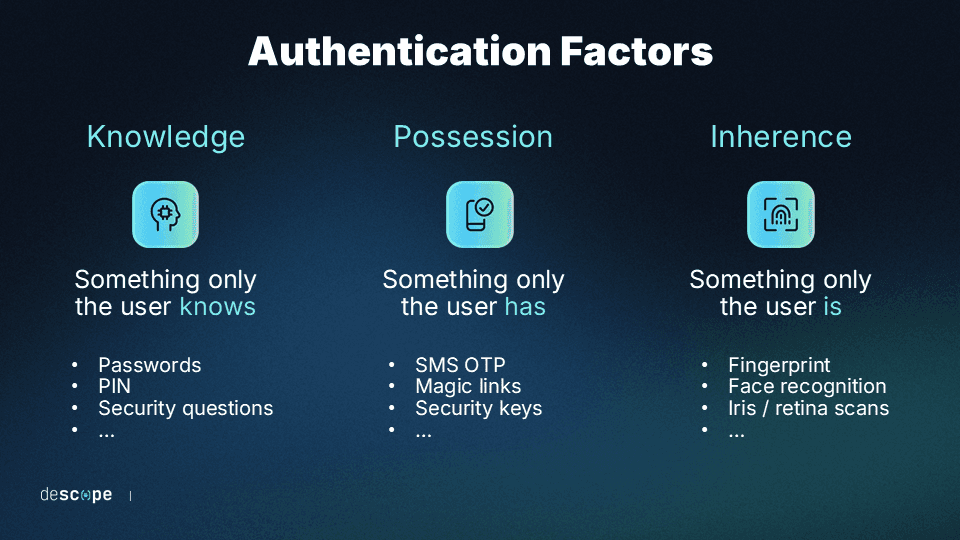
Having MFA virtually means that even if an attacker gets to a user's password through phishing or other means, they still cannot access the system without the other verification factors, which are typically “something the user is or has,” such as a biometric fingerprint scan, a hardware token, or a one-time code sent to the user’s mobile device.
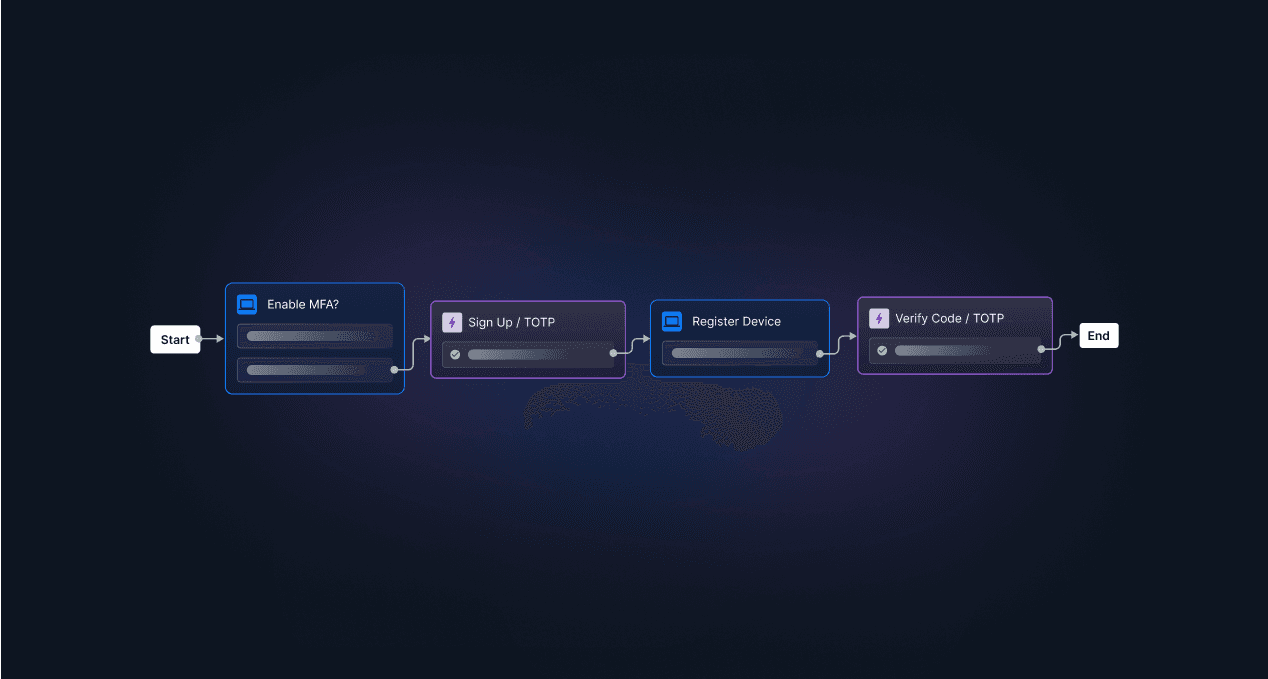
While many baseline MFA deployments remain susceptible to social engineering schemes, deploying a more adaptive, phishing-resistant approach to MFA is the best way to maximize this benefit.
Streamlined compliance
MFA also helps organizations meet the security and privacy needs of regulatory frameworks. Implementing MFA helps organizations manage security risks effectively and creates an auditable trail to demonstrate compliance during potential audits.
Depending on the industry or location, many kinds of regulations might apply to you. Some of the most common include:
General Data Protection Regulation GDPR: Focuses on the protection of personal data and privacy in the European Union.
Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS): For ecommerce, retail and businesses that process payment card data, the PCI DSS applies.
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): Mandates the protection of sensitive patient health information in the healthcare industry.
Financial Regulation: Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) requires stringent internal access controls to financial reporting in publicly traded companies. The Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council (FFIEC) Guidance strongly recommends MFA for financial institutions, like banks, to protect their customer information.
In many cases, multiple overlapping frameworks will apply simultaneously.
And MFA is an explicit or de facto requirement in many regulatory frameworks. Failure to meet a given regulation’s requirements for MFA or access control more broadly can lead to direct financial and other penalties. For example, HIPAA non-compliance fines for 2023 range from $127 to $1,919,173 per violation, and criminal charges may be applied in the worst cases.
MFA is one of the best authentication methods for strengthening compliance enforcement for your software, its adopters, its end users, and all other stakeholders.
Remote accessibility
One benefit of MFA that has come into sharp distinction in recent years is its aptitude for enabling remote work. MFA supports a flexible and secure remote work model, facilitating productivity without compromising security.
Organizations’ on-premise cybersecurity measures often cannot extend to employees’ home (or other) environments beyond the reach of firewalls and content filters. Access control, particularly MFA, is one of a few ways remote or cloud-based work can happen securely.
The flexibility of MFA allows employees to securely access necessary systems and data from any location while using different devices. By integrating MFA, organizations can maintain a high level of security irrespective of the employee's work location.
Scalability and adaptability
One under-appreciated aspect of MFA is that it is almost infinitely customizable and scalable. With cyber threats constantly evolving, organizations need identity and access management that can adapt to new risks. Modern MFA solutions offer a range of authentication methods, allowing companies to upgrade or change methods as security needs grow. This flexibility is particularly valuable in high-risk industries like finance and healthcare, where security requirements often tighten over time.
MFA can be tailored to fit specific organizational needs and risk profiles, with features such as step-up authentication that accounts for differing sensitivity and risk profiles for different users.
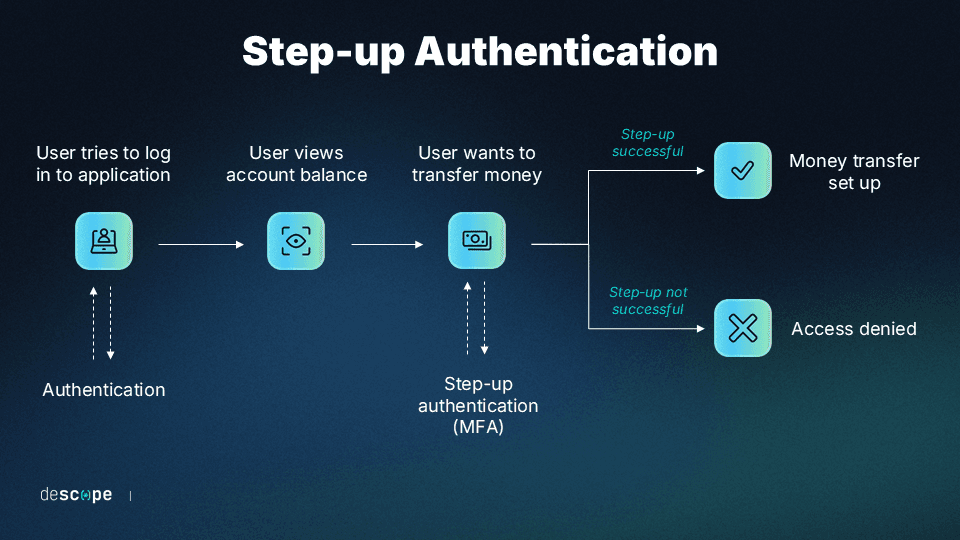
MFA has the capacity to scale with organizational growth and evolving security requirements across thousands of users, devices, and applications, providing robust security without the need for extensive individual configuration.
User convenience
Last but not least, one of the most easily recognizable benefits of MFA is the convenience it provides for the users of your app or website. Despite initial perceptions of added complexity, MFA can actually streamline the authentication process, offering a smoother user experience.
Traditional security measures, like passwords, can be cumbersome and lead to user frustration, especially when users are required to change passwords frequently. Since MFA doesn’t rely solely on passwords, it reduces the burden on users to remember complex combinations.
And this doesn’t just benefit users; if you opt for passwordless MFA, it also reduces the burden of password management for IT staff.
Of course, convenience does sometimes come at a cost. MFA deployments that are either too simple or too complicated can run the risk of MFA fatigue, which is both a condition and an attack that can lead to broken authentication.
That’s why it’s important to balance user-friendly features against robust security measures. One way to do this is through risk-based authentication or adaptive authentication measures that take the user behavior into account before presenting an MFA flow. This means that returning legitimate users do not have to go through the MFA process every time, improving their experience. At the same time, risky or suspicious logins are always put through an MFA flow.
Reap the benefits of MFA with Descope
Want to reap the full extent of MFA benefits?
Descope helps developers and IT teams easily add MFA to their apps using no-code workflows. Admins can pick from a wide variety of methods – both passwords and passwordless – and create risk-based MFA flows in a visual editor to ensure that MFA is only enforced for risky sessions.
Descope also integrates with specialized risk services such as Google reCAPTCHA Enterprise, Traceable, and Have I Been Pwned to ingest granular risk scores and create branching user journey paths based on the risk of the login attempt.
Sign up for a Descope Free Forever account to implement MFA for your project in minutes. Have questions about our platform? Book time with our auth experts to learn more.